Starting a wood preservation and protection process first requires the ability to correctly identify what is causing the damage.
Infestation analysis is the fundamental step to determine which family of insects is responsible, assess the severity of the damage, and define the most suitable treatment program.
Wood-boring insects are not all the same: each group has different biological characteristics, habits, and preferences that influence the type of intervention required.
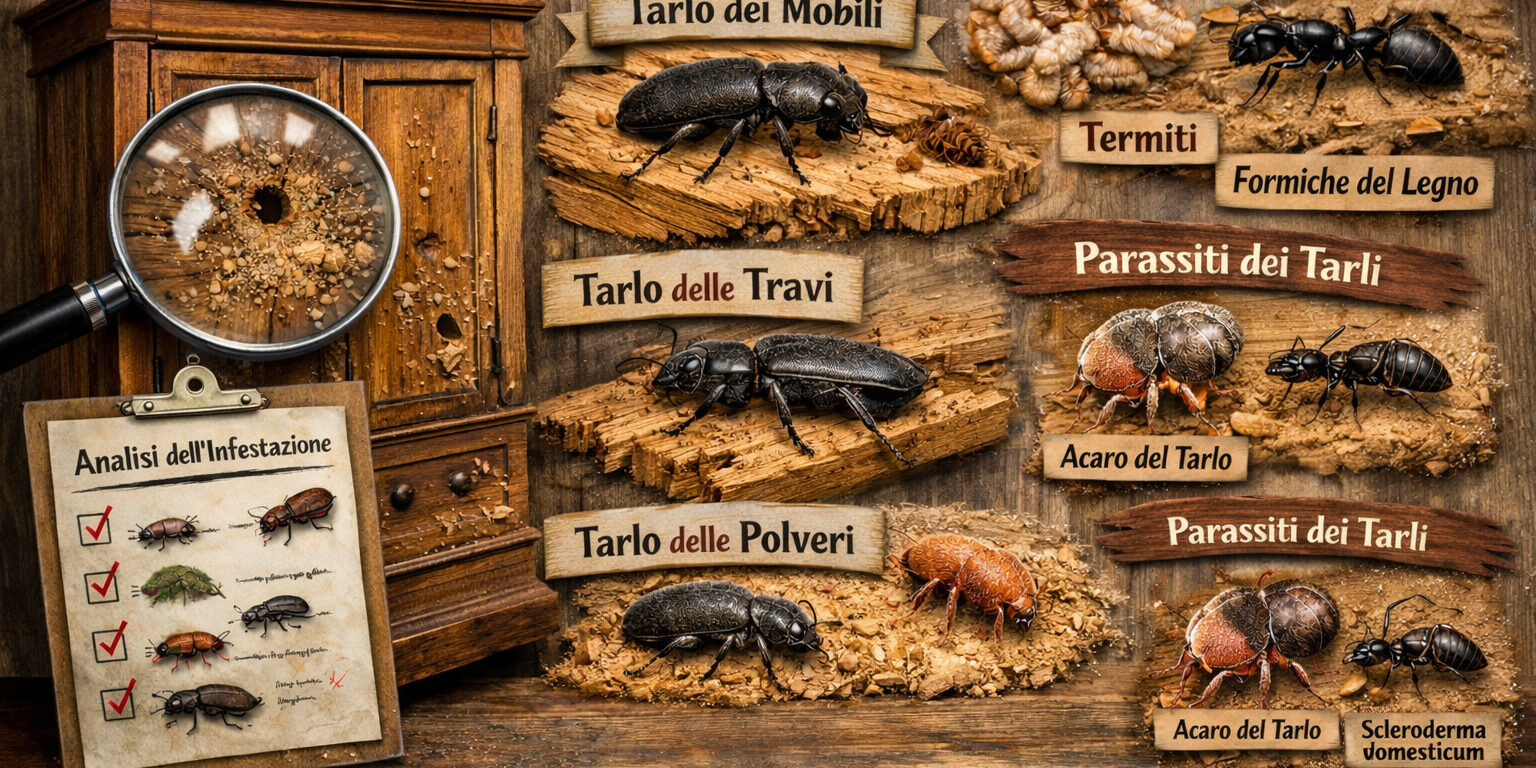
The main families of woodworms (wood-boring beetles)
Woodworms are a diverse group of insects capable of causing serious damage to furniture, structural elements, and wooden artifacts.
The three main families responsible for domestic infestations are:
-
Anobiidae (furniture beetle): the most common and widespread group. It includes species such as Anobium punctatum and Xestobium rufovillosum, also known as the “deathwatch beetle” for the characteristic ticking sound produced by adults.
They mainly attack softwood and are often found in furniture, beams, floors, and wooden fixtures.
Their presence is indicated by small round exit holes (1–2 mm) and fine, talc-like wood dust. -
Cerambycidae (house longhorn beetle): the best-known species is Hylotrupes bajulus, commonly called the house longhorn beetle.
It primarily attacks structural timber, creating deep tunnels that can reduce the mechanical strength of beams and floors, potentially compromising building safety. -
Lyctidae (powderpost beetles): such as Lyctus brunneus, these insects prefer hardwoods like oak, walnut, and mahogany.
Their larvae turn the interior of the wood into a very fine powder, causing both aesthetic and structural damage.
Not only woodworms: other wood-boring insects
It is important not to confuse woodworms with other organisms that attack wood, such as termites or carpenter ants.
These insects have different behaviors, life cycles, and infestation methods, and therefore require specific control strategies.
A correct diagnosis prevents ineffective treatments and wasted time.
Woodworm parasites and possible risks
Inside the tunnels created by woodworms, some woodworm parasites may also live. These are insects or mites that feed on woodworm larvae.
The most common include:
- Scleroderma domesticum
- Pyemotes ventricosus (woodworm mite)
Although they do not feed on wood, these organisms can cause unpleasant skin irritations and dermatitis in people living in infested environments.
Toward the solution: W13 microwave treatment
Once the insect responsible for the infestation has been accurately identified, targeted and effective action can be taken.
W13 offers microwave treatment for wood disinfestation, an advanced technology that eliminates woodworms, larvae, eggs, and parasites through controlled heating of the material.
Microwaves penetrate deep into the wood, rapidly raising the internal temperature to levels lethal for insects, without the use of chemical substances.
This system is:
- Eco-friendly and residue-free
- Fast and targeted
- Suitable for furniture, beams, floors, and structural elements
In future articles, we will explain how to recognize the signs of an active infestation and when it is advisable to rely on a specialized professional service.